
| 情報学部 | 菅沼ホーム | 全体目次 | 演習解答例 | 付録 | 索引 |

[メソッド修飾子] メソッドの型 メソッド名 ( 引数リスト )


/****************************/
/* nの階乗の計算 */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
/*
データの入力
*/
System.out.print("nの値を入力して下さい ");
int n = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
/*
階乗の計算
*/
double kai = 1.0; // 初期設定
for (int i1 = 1; i1 <= n; i1++)
kai *= (double)i1;
/*
結果の出力
*/
System.out.println(" " + n + "の階乗は=" + kai);
}
}

01 /****************************/
02 /* nの階乗の計算 */
03 /* coded by Y.Suganuma */
04 /****************************/
05 import java.io.*;
06
07 public class Test {
08 public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
09 {
10 BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
11 /*
12 データの入力
13 */
14 System.out.print("nの値を入力して下さい ");
15 int n = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
16 /*
17 階乗の計算
18 */
19 double kai = kaijo(n); // kai = (new Test()).kaijo(n); のようにすれば,
20 // メソッドkaijoに対するstatic宣言は不要
21 /*
22 結果の出力
23 */
24 System.out.println(" " + n + "の階乗は=" + kai);
25 }
26
27 /**************************/
28 /* mの階乗 */
29 /* m : データ */
30 /* return : nの階乗 */
31 /**************************/
32 static double kaijo(int m)
33 {
34 double s = 1.0;
35 for (int i1 = 1; i1 <= m; i1++)
36 s *= (double)i1;
37 return s;
38 }
39 }
System.out.println(" " + n + "の階乗は=" + kaijo(n));
/****************************/
/* nの階乗の計算 */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
Exam ex = new Exam();
}
}
class Exam
{
Exam() throws IOException
{
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
/*
データの入力
*/
System.out.print("nの値を入力して下さい ");
int n = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
/*
階乗の計算
*/
double kai = kaijo(n); // kai = (new Test()).kaijo(n); のようにすれば,
// メソッドkaijoに対するstatic宣言は不要
/*
結果の出力
*/
System.out.println(" " + n + "の階乗は=" + kai);
}
/**************************/
/* mの階乗 */
/* m : データ */
/* return : nの階乗 */
/**************************/
double kaijo(int m)
{
double s = 1.0;
for (int i1 = 1; i1 <= m; i1++)
s *= (double)i1;
return s;
}
}

/****************************/
/* nの階乗の計算 */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
/*
データの入力
*/
System.out.print("nの値を入力して下さい ");
int n = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
/*
階乗の計算
*/
double kai = kaijo(n);
/*
結果の出力
*/
System.out.println(" " + n + "の階乗は=" + kai);
}
/**************************/
/* mの階乗 */
/* m : データ */
/* return : nの階乗 */
/**************************/
static double kaijo(int m)
{
double s;
if (m > 1)
s = m * kaijo(m-1); // 自分自身を呼んでいる
else
s = 1;
return s;
}
}

/****************************/
/* nCrの計算 */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
/*
データの入力
*/
System.out.print("nの値は? ");
int n = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
System.out.print("rの値は? ");
int r = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
/*
nCrの計算と出力
*/
double sn = kaijo(n);
double sr = kaijo(r);
double snr = kaijo(n-r);
System.out.println(" " + n + "C" + r + "は=" + sn/(sr*snr));
}
/**************************/
/* mの階乗 */
/* m : データ */
/* return : nの階乗 */
/**************************/
static double kaijo(int m)
{
double s = 1.0;
for (int i1 = 1; i1 <= m; i1++)
s *= (double)i1;
return s;
}
}

01 [クラス修飾子] class クラス名 {
02 // クラス本体(変数やメソッドの定義,定義の順番は任意)
03 [変数修飾子] データ型 変数名1,・・・;
04 [変数修飾子] データ型 変数名2,・・・;
05 ・・・・・
06 [メソッド修飾子] メソッドの型 メソッド名1 (引数の並び) {
07 データ型 変数名1,・・・;
08 メソッドにおける処理
09 }
10 [メソッド修飾子] メソッドの型 メソッド名2 (引数の並び) {
11 データ型 変数名A,・・・;
12 メソッドにおける処理
13 }
14 ・・・・・
15 }
EXample ex = new Example; // ex は Example 型オブジェクトへのポインタと見て良い ex.x = 20; // クラス内に定義されている変数 x の参照 y = ex.func(10); // クラス内に定義されているメソッド func の参照
c1 = new Complex(); c1.re = 1.0; c1.im = 2.0;
01 import java.io.*;
02
03 class Complex {
04 public double re, im;
05 public Complex (double x, double y) // コンストラクタ
06 {
07 re = x;
08 im = y;
09 }
10 }
11
12 public class Test {
13 public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
14 {
15 Complex c1 = new Complex(1.0, 2.0); // コンストラクタにより,変数 re,im に 1,2 を設定
16 double x = 10.0;
17 System.out.printf("変更前 c1 = %f %f x = %f\n", c1.re, c1.im, x);
18 Complex c2 = c1;
19 double y = x;
20 System.out.printf("変更前 c2 = %f %f y = %f\n", c2.re, c2.im, y);
21 c2.re = 3.0;
22 c2.im = 4.0;
23 y = 20.0;
24 System.out.printf("変更後 c1 = %f %f x = %f\n", c1.re, c1.im, x);
25 System.out.printf("変更後 c2 = %f %f y = %f\n", c2.re, c2.im, y);
26 }
27 }
変更前 c1 = 1.000000 2.000000 x = 10.000000 変更前 c2 = 1.000000 2.000000 y = 10.000000 変更後 c1 = 3.000000 4.000000 x = 10.000000 変更後 c2 = 3.000000 4.000000 y = 20.000000
01 #include <stdio.h>
02
03 class Complex {
04 public :
05 double re, im;
06 Complex () {} // コンストラクタ
07 Complex (double x, double y) // コンストラクタ
08 {
09 re = x;
10 im = y;
11 }
12 }; // セミコロンを忘れないこと
13
14 int main()
15 {
16 Complex *c1 = new Complex(1, 2); // コンストラクタにより,変数 re,im に 1,2 を設定
17 Complex c3 = Complex(1, 2); // コンストラクタにより,変数 re,im に 1,2 を設定
18 double x = 10.0;
19 printf("変更前 c1 = %f %f c3 = %f %f x = %f\n", c1->re, c1->im, c3.re, c3.im, x);
20 Complex *c2 = c1;
21 Complex c4 = c3;
22 double y = x;
23 printf("変更前 c2 = %f %f c4 = %f %f y = %f\n", c2->re, c2->im, c4.re, c4.im, y);
24 c2->re = 3.0;
25 c2->im = 4.0;
26 c4.re = 3.0;
27 c4.im = 4.0;
28 y = 20.0;
29 printf("変更後 c1 = %f %f c3 = %f %f x = %f\n", c1->re, c1->im, c3.re, c3.im, x);
30 printf("変更後 c2 = %f %f c4 = %f %f y = %f\n", c2->re, c2->im, c4.re, c4.im, y);
31 return 0;
32 }
変更前 c1 = 1.000000 2.000000 c3 = 1.000000 2.000000 x = 10.000000 変更前 c2 = 1.000000 2.000000 c4 = 1.000000 2.000000 y = 10.000000 変更後 c1 = 3.000000 4.000000 c3 = 1.000000 2.000000 x = 10.000000 変更後 c2 = 3.000000 4.000000 c4 = 3.000000 4.000000 y = 20.000000

/****************************/
/* private 変数 */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
import java.io.*;
/***********************/
/* クラスExampleの定義 */
/***********************/
class Example {
private int x; // private 変数
int y; // 変数
// メソッド,値の設定
void v_set1()
{
x = 10; // クラス内のメソッドからは参照可能
y = 20;
}
// メソッド,値の設定
void v_set2()
{
x = 30; // クラス内のメソッドからは参照可能
y = 40;
}
// メソッド,値の出力
void output()
{
System.out.println(" x = " + x + ", y = " + y);
}
}
/**************************************/
/* mainメソッドを含むクラスTestの定義 */
/**************************************/
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
Example t1 = new Example(); // Example 型オブジェクトの生成
// 下の 2 行のように書いても良い
Example t2; // Example 型オブジェクトであることの宣言
t2 = new Example(); // Example 型オブジェクトの生成
t1.v_set1(); // メソッドの呼び出し
t2.v_set2(); // メソッドの呼び出し
System.out.println("オブジェクト t1");
System.out.println(" y = " + t1.y); // 変数 y の参照,変数 x の参照はできない
t1.output();
System.out.println("オブジェクト t2");
System.out.println(" y = " + t2.y); // 変数 y の参照,変数 x の参照はできない
t2.output();
}
}
オブジェクト t1 y = 20 x = 10, y = 20 オブジェクト t2 y = 40 x = 30, y = 40

/****************************/
/* final,static */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
import java.io.*;
/****************************/
/* クラスFinalExampleの定義 */
/****************************/
final class FinalExample // このクラスを拡張できない(継承できない)
{
static String msg = "final class"; // 静的変数
// インスタンスメソッド
void func()
{
System.out.println("FinalExample のインスタンスメソッド");
}
// 静的メソッド
static void static_func()
{
System.out.println("FinalExample の静的メソッド");
}
}
/***********************/
/* クラスExampleの定義 */
/***********************/
class Example
{
static int count; // 静的変数
final int x = 10; // 定数,値を変更できない
int y = 20; // インスタンス変数
// コンストラクタ,インスタンスが生成される度に count を増加
Example ()
{
count++;
}
// インスタンスメソッド
void func()
{
System.out.println("インスタンスメソッド");
}
// 静的メソッド
static void static_func()
{
System.out.println("静的メソッド");
}
}
/**************************************/
/* mainメソッドを含むクラスTestの定義 */
/*************************************/
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
// final クラス
System.out.println(" *** final クラス ***");
FinalExample fe = new FinalExample();
System.out.println(fe.msg);
System.out.println(FinalExample.msg); // 静的変数はこのように参照するのが一般的
fe.func(); // インスタンスメソッドの呼び出し
fe.static_func(); // 静的メソッドの呼び出し
FinalExample.static_func(); // 静的メソッドの呼び出し(こちらの方が一般的)
// final でないクラス
System.out.println(" *** final でないクラス ***");
Example.count = 0;
Example ex1 = new Example(); // count の値は 1 になる
Example ex2 = new Example(); // count の値は 2 になる
// ex2.x = 100; // 値を変更することは出来ない
ex2.y = 200;
System.out.println("x = " + ex1.x + " y = " + ex1.y + " count = " + Example.count);
System.out.println("x = " + ex2.x + " y = " + ex2.y + " count = " + Example.count);
ex2.func(); // インスタンスメソッドの呼び出し
Example.static_func(); // 静的メソッドの呼び出し
// クラス Test 内のメソッドの利用
System.out.println(" *** クラス Test 内のメソッド ***");
// message(); // インスタンスメソッドの呼び出し.main メソッド(このメソッド)は
// static であるので static でないメソッドを直接呼び出せない
static_message(); // 静的メソッドの呼び出し
}
// インスタンスメソッド
void message ()
{
System.out.println("main から インスタンスメソッドの呼び出し");
}
// 静的メソッド
static void static_message ()
{
System.out.println("main から 静的メソッドの呼び出し");
}
}
*** final クラス *** final class final class FinalExample のインスタンスメソッド FinalExample の静的メソッド FinalExample の静的メソッド *** final でないクラス *** x = 10 y = 20 count = 2 x = 10 y = 200 count = 2 インスタンスメソッド 静的メソッド *** クラス Test 内のメソッド *** main から 静的メソッドの呼び出し

t1.v_set1(); t2.v_set2();
Example (int x, int y) // コンストラクタ
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
Example t1 = new Example(10, 20); // Example 型オブジェクトの生成
// 下の 2 行のように書いても良い
Example t2; // Example 型オブジェクトであることの宣言
t2 = new Example(30, 40); // Example 型オブジェクトの生成
Example(int x1, int y1)
{
x = x1;
y = y1;
}

01 /****************************/
02 /* 時間データの処理 */
03 /* coded by Y.Suganuma */
04 /****************************/
05 import java.io.*;
06
07 /********************/
08 /* クラスTimeの宣言 */
09 /********************/
10 class Time {
11 int hour, min, sec;
12 // コンストラクタ1
13 Time(int h, int m, int s)
14 {
15 hour = h;
16 min = m;
17 sec = s;
18 }
19 // コンストラクタ2
20 Time(int h, int m)
21 {
22 hour = h;
23 min = m;
24 }
25 // コンストラクタ3
26 Time() {}
27 }
28
29 /**************************************/
30 /* mainメソッドを含むクラスTestの定義 */
31 /**************************************/
32 public class Test {
33 public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
34 {
35 Time t1 = new Time(10, 20, 23); // 10:20:23
36 System.out.println(t1.hour + ":" + t1.min + ":" + t1.sec);
37 Time t2 = new Time(12, 30); // sec は 0 に初期設定される
38 System.out.println(t2.hour + ":" + t2.min + ":" + t2.sec);
39 Time t3 = new Time(); // hour,min,sec がすべて 0 に設定される
40 System.out.println(t3.hour + ":" + t3.min + ":" + t3.sec);
41 }
42 }
10:20:23 12:30:0 0:0:0

01 /****************************/
02 /* 様々なデータ型の引き渡し */
03 /* coded by Y.Suganuma */
04 /****************************/
05 import java.io.*;
06
07 /***********************/
08 /* クラスComplexの定義 */
09 /***********************/
10 class Complex {
11 double re, im;
12 // コンストラクタ
13 Complex(double re, double im)
14 {
15 this.re = re;
16 this.im = im;
17 }
18 }
19
20 /**************************************/
21 /* mainメソッドを含むクラスTestの定義 */
22 /**************************************/
23 public class Test {
24 public static void main(String args[])
25 {
26 int a = 1;
27 int ar_1 [] = {10, 20};
28 int ar_2 [][] = {{100, 200, 300}, {400, 500, 600}};
29 Complex cx = new Complex(1000, 2000);
30 // メソッドを呼ぶ前の状態
31 System.out.println(" ***メソッドを呼ぶ前の状態***");
32 System.out.println("a = " + a);
33 System.out.println("ar_1[0] = " + ar_1[0] + ", ar_1[1] = " + ar_1[1]);
34 for (int i1 = 0; i1 < 2; i1++) {
35 for (int i2 = 0; i2 < 3; i2++) {
36 if (i2 < 2)
37 System.out.print("ar_2[" + i1 + "][" + i2 + "] = " + ar_2[i1][i2] + ", ");
38 else
39 System.out.println("ar_2[" + i1 + "][" + i2 + "] = " + ar_2[i1][i2]);
40 }
41 }
42 System.out.println("cx.re = " + cx.re + ", cx.im = " + cx.im);
43 // メソッドを呼ぶ
44 method(a, ar_1, ar_2, cx);
45 // メソッドを呼んだ後の状態
46 System.out.println(" ***メソッドを呼んだ後の状態***");
47 System.out.println("a = " + a);
48 System.out.println("ar_1[0] = " + ar_1[0] + ", ar_1[1] = " + ar_1[1]);
49 for (int i1 = 0; i1 < 2; i1++) {
50 for (int i2 = 0; i2 < 3; i2++) {
51 if (i2 < 2)
52 System.out.print("ar_2[" + i1 + "][" + i2 + "] = " + ar_2[i1][i2] + ", ");
53 else
54 System.out.println("ar_2[" + i1 + "][" + i2 + "] = " + ar_2[i1][i2]);
55 }
56 }
57 System.out.println("cx.re = " + cx.re + ", cx.im = " + cx.im);
58 }
59
60 /******************************************/
61 /* メソッドの例 */
62 /* a : int 型 */
63 /* ar_1 : int 型 1 次元配列 */
64 /* ar_2 : int 型 2 次元配列 */
65 /* cx : Complex クラスのオブジェクト */
66 /******************************************/
67 static void method(int a, int ar_1[], int ar_2[][], Complex cx)
68 {
69 a = 9;
70 ar_1[0] = 99;
71 ar_2[1][0] = 999;
72 cx.im = 9999;
73 }
74 }
01 ***メソッドを呼ぶ前の状態*** 02 a = 1 03 ar_1[0] = 10, ar_1[1] = 20 04 ar_2[0][0] = 100, ar_2[0][1] = 200, ar_2[0][2] = 300 05 ar_2[1][0] = 400, ar_2[1][1] = 500, ar_2[1][2] = 600 06 cx.re = 1000.0, cx.im = 2000.0 07 ***メソッドを呼んだ後の状態*** 08 a = 1 09 ar_1[0] = 99, ar_1[1] = 20 10 ar_2[0][0] = 100, ar_2[0][1] = 200, ar_2[0][2] = 300 11 ar_2[1][0] = 999, ar_2[1][1] = 500, ar_2[1][2] = 600 12 cx.re = 1000.0, cx.im = 9999.0

/****************************/
/* 複数結果の受け取り */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
import java.io.*;
/**************************************/
/* mainメソッドを含むクラスTestの定義 */
/**************************************/
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a = 10, b = 20;
int wa_sa [] = new int [2];
// メソッドを呼ぶ
double seki_sho [] = cal(a, b, wa_sa);
// 結果
System.out.println(a + " と " + b + " の");
System.out.println(" 和は " + wa_sa[0]);
System.out.println(" 差は " + wa_sa[1]);
System.out.println(" 積は " + seki_sho[0]);
System.out.println(" 商は " + seki_sho[1]);
}
/******************************/
/* 2 つのデータの加減乗除 */
/* a, b : データ */
/* wa_sa : a+b, a-b */
/* return : a*b, a/b */
/******************************/
static double [] cal(int a, int b, int wa_sa [])
{
wa_sa[0] = a + b;
wa_sa[1] = a - b;
double seki_sho [] = new double [2];
seki_sho[0] = a * b;
seki_sho[1] = (double)a / b;
return seki_sho;
}
}
int (*sub)(double, char *)
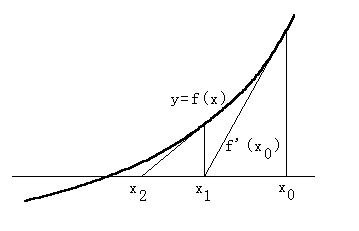
f1(x) = ex - 3x = 0 と f2(x) = sin(x) - 0.5 = 0
xn+1 = xn - f(xn) / f'(xn)
001 /****************************/
002 /* 関数名の受け渡し */
003 /* coded by Y.Suganuma */
004 /****************************/
005 #include <stdio.h>
006 #include <math.h>
007
008 /****************************/
009 /* 関数値及びその微分の計算 */
010 /****************************/
011 // f(x) = sin(x) - 0.5
012 double snx1(double x)
013 {
014 double y= exp(x) - 3.0 * x;
015 return y;
016 }
017
018 double dsnx1(double x)
019 {
020 double y = exp(x) - 3.0;
021 return y;
022 }
023 // f(x) = sin(x) - 0.5
024 double snx2(double x)
025 {
026 double y= sin(x) - 0.5;
027 return y;
028 }
029
030 double dsnx2(double x)
031 {
032 double y = cos(x);
033 return y;
034 }
035
036 /*****************************************************/
037 /* Newton法による非線形方程式(f(x)=0)の解 */
038 /* fn : f(x)を計算する関数名 */
039 /* dfn : f(x)の微分を計算する関数名 */
040 /* x0 : 初期値 */
041 /* eps1 : 終了条件1(|x(k+1)-x(k)|<eps1) */
042 /* eps2 : 終了条件2(|f(x(k))|<eps2) */
043 /* max : 最大試行回数 */
044 /* ind : 実際の試行回数 */
045 /* (負の時は解を得ることができなかった) */
046 /* return : 解 */
047 /*****************************************************/
048 double newton(double(*f)(double), double(*df)(double), double x0,
049 double eps1, double eps2, int max, int *ind)
050 {
051 double x1 = x0;
052 double x = x1;
053 int sw = 0;
054 *ind = 0;
055
056 while (sw == 0 && *ind >= 0) {
057
058 sw = 1;
059 *ind += 1;
060 double g = f(x1);
061
062 if (fabs(g) > eps2) {
063 if (*ind <= max) {
064 double dg = df(x1);
065 if (fabs(dg) > eps2) {
066 x = x1 - g / dg;
067 if (fabs(x-x1) > eps1 && fabs(x-x1) > eps1*fabs(x)) {
068 x1 = x;
069 sw = 0;
070 }
071 }
072 else
073 *ind = -1;
074 }
075 else
076 *ind = -1;
077 }
078 }
079
080 return x;
081 }
082
083 /*******************/
084 /* main プログラム */
085 /*******************/
086 int main()
087 {
088 double eps1 = 1.0e-7;
089 double eps2 = 1.0e-10;
090 double x0 = 0.0;
091 int max = 30;
092 int ind;
093 // f(x) = sin(x) - 0.5 = 0 の解
094 double x = newton(snx1, dsnx1, x0, eps1, eps2, max, &ind);
095
096 printf("exp(x) - 3.0 * x = 0\n");
097 printf(" ind = %d, x = %.3f, f(x) = %.3f, f'(x) = %.3f\n", ind, x, snx1(x), dsnx1(x));
098 // f(x) = sin(x) - 0.5 = 0 の解
099 x = newton(snx2, dsnx2, x0, eps1, eps2, max, &ind);
100
101 printf("sin(x) - 0.5 = 0\n");
102 double PI = 4.0 * atan(1.0);
103 printf(" ind = %d, x = %.3f, f(x) = %.3f, f'(x) = %.3f\n", ind, 180*x/PI, snx2(x), dsnx2(x));
104
105 return 0;
106 }
exp(x) - 3.0 * x = 0 ind = 5, x = 0.619, f(x) = 0.000, f'(x) = -1.143 sin(x) - 0.5 = 0 ind = 4, x = 30.000, f(x) = -0.000, f'(x) = 0.866
01 /****************************/
02 /* ニュートン法 */
03 /* coded by Y.Suganuma */
04 /****************************/
05 import java.io.*;
06
07 public class Test {
08 public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
09 {
10 double eps1 = 1.0e-7;
11 double eps2 = 1.0e-10;
12 double x0 = 0.0;
13 int max = 30;
14 int ind[] = new int [1];
15 // f(x) = exp(x) - 3.0 * x = 0 の解
16 // 関数値を計算するクラス
17 Func kn1 = new Func(1);
18 Func kn2 = new Func(2);
19 // ニュートン法の実行
20 double x = Math_ex.newton(x0, eps1, eps2, max, ind, kn1, kn2);
21 // 出力
22 System.out.printf("exp(x) - 3.0 * x = 0\n");
23 System.out.printf(" ind = %d, x = %.3f, f(x) = %.3f, f'(x) = %.3f\n", ind[0], x, kn1.snx(x), kn2.snx(x));
24 // f(x) = sin(x) - 0.5 = 0 の解
25 // 関数値を計算するクラス
26 Func kn3 = new Func(3);
27 Func kn4 = new Func(4);
28 // ニュートン法の実行
29 x = Math_ex.newton(x0, eps1, eps2, max, ind, kn3, kn4);
30 // 出力
31 System.out.printf("sin(x) - 0.5 = 0\n");
32 System.out.printf(" ind = %d, x = %.3f, f(x) = %.3f, f'(x) = %.3f\n", ind[0], 180*x/Math.PI, kn3.snx(x), kn4.snx(x));
33 }
34 }
35
36 /******************************/
37 /* 関数値およびその微分の計算 */
38 /******************************/
39 class Func {
40 private int sw;
41 // コンストラクタ
42 Func (int s) {sw = s;}
43 // double型メソッド
44 double snx(double x)
45 {
46
47 double y = 0.0;
48
49 switch (sw) {
50 // 関数 f(x) = exp(x) - 3.0 * x の計算
51 case 1:
52 y = Math.exp(x) - 3.0 * x;
53 break;
54 // 関数 f(x) = exp(x) - 3.0 * x の微分の計算
55 case 2:
56 y = Math.exp(x) - 3.0;
57 break;
58 // 関数 f(x) = Math.sin(x) - 0.5 の計算
59 case 3:
60 y = Math.sin(x) - 0.5;
61 break;
62 // 関数 f(x) = Math.sin(x) - 0.5 の微分の計算
63 case 4:
64 y = Math.cos(x);
65 break;
66 }
67
68 return y;
69 }
70 }
--------------------------------
/************************
/* 科学技術計算用の手法 */
/************************/
public final class Math_ex {
/*****************************************************/
/* Newton法による非線形方程式(f(x)=0)の解 */
/* x1 : 初期値 */
/* eps1 : 終了条件1(|x(k+1)-x(k)|<eps1) */
/* eps2 : 終了条件2(|f(x(k))|<eps2) */
/* max : 最大試行回数 */
/* ind : 実際の試行回数 */
/* (負の時は解を得ることができなかった) */
/* kn1 : 関数を計算するクラスオブジェクト */
/* kn2 : 関数の微分を計算するクラスオブジェクト */
/* return : 解 */
/*****************************************************/
static double newton(double x1, double eps1, double eps2, int max,
int ind[], Func kn1, Func kn2)
{
double x = x1;
int sw = 0;
ind[0] = 0;
while (sw == 0 && ind[0] >= 0) {
ind[0]++;
sw = 1;
double g = kn1.snx(x1);
if (Math.abs(g) > eps2) {
if (ind[0] <= max) {
double dg = kn2.snx(x1);
if (Math.abs(dg) > eps2) {
x = x1 - g / dg;
if (Math.abs(x-x1) > eps1 && Math.abs(x-x1) > eps1*Math.abs(x)) {
x1 = x;
sw = 0;
}
}
else
ind[0] = -1;
}
else
ind[0] = -1;
}
}
return x;
}
}
exp(x) - 3.0 * x = 0 ind = 5, x = 0.619, f(x) = -0.000, f'(x) = -1.143 sin(x) - 0.5 = 0 ind = 4, x = 30.000, f(x) = -0.000, f'(x) = 0.866
/****************************/
/* ニュートン法 */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
double eps1 = 1.0e-7;
double eps2 = 1.0e-10;
double x0 = 0.0;
int max = 30;
int ind[] = new int [1];
// f(x) = exp(x) - 3.0 * x = 0 の解
// 関数値を計算するクラス
Kansu1 kn1 = new Kansu1();
// ニュートン法の実行
double x = kn1.newton(x0, eps1, eps2, max, ind);
// 出力
System.out.printf("exp(x) - 3.0 * x = 0\n");
System.out.printf(" ind = %d, x = %.3f, f(x) = %.3f, f'(x) = %.3f\n", ind[0], x, kn1.snx(x), kn1.dsnx(x));
// f(x) = sin(x) - 0.5 = 0 の解
// 関数値を計算するクラス
Kansu2 kn2 = new Kansu2();
// ニュートン法の実行
x = kn2.newton(x0, eps1, eps2, max, ind);
// 出力
System.out.printf("sin(x) - 0.5 = 0\n");
System.out.printf(" ind = %d, x = %.3f, f(x) = %.3f, f'(x) = %.3f\n", ind[0], 180*x/Math.PI, kn2.snx(x), kn2.dsnx(x));
}
}
/******************************/
/* 関数値およびその微分の計算 */
/******************************/
// f(x) = exp(x) - 3.0 * x = 0 の解
class Kansu1 extends Newton // クラスNewtonを継承
{
// 関数値(f(x))の計算
double snx(double x) // クラスNewtonのメソッドのオーバーライド
{
double y = Math.exp(x) - 3.0 * x;
return y;
}
// 関数の微分の計算
double dsnx(double x) // クラスNewtonのメソッドのオーバーライド
{
double y = Math.exp(x) - 3.0;
return y;
}
}
// f(x) = sin(x) - 0.5 = 0 の解
class Kansu2 extends Newton // クラスNewtonを継承
{
// 関数値(f(x))の計算
double snx(double x) // クラスNewtonのメソッドのオーバーライド
{
double y = Math.sin(x) - 0.5;
return y;
}
// 関数の微分の計算
double dsnx(double x) // クラスNewtonのメソッドのオーバーライド
{
double y = Math.cos(x);
return y;
}
}
/*****************************************************/
/* Newton法による非線形方程式(f(x)=0)の解 */
/* x1 : 初期値 */
/* eps1 : 終了条件1(|x(k+1)-x(k)|<eps1) */
/* eps2 : 終了条件2(|f(x(k))|<eps2) */
/* max : 最大試行回数 */
/* ind : 実際の試行回数 */
/* (負の時は解を得ることができなかった) */
/* return : 解 */
/*****************************************************/
abstract class Newton {
abstract double snx(double x); // 定義しておく必要あり
abstract double dsnx(double x); // 定義しておく必要あり
double newton(double x1, double eps1, double eps2, int max, int ind[])
{
double x = x1;
int sw = 0;
ind[0] = 0;
while (sw == 0 && ind[0] >= 0) {
ind[0]++;
sw = 1;
double g = snx(x1);
if (Math.abs(g) > eps2) {
if (ind[0] <= max) {
double dg = dsnx(x1);
if (Math.abs(dg) > eps2) {
x = x1 - g / dg;
if (Math.abs(x-x1) > eps1 && Math.abs(x-x1) > eps1*Math.abs(x)) {
x1 = x;
sw = 0;
}
}
else
ind[0] = -1;
}
else
ind[0] = -1;
}
}
return x;
}
}
インタフェース名 ラムダ式名 = ( 引数 ) -> { 処理 } java.lang.Comparable java.lang.Runnable
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[])
{
Runnable lam = () -> { System.out.println("Runnable を利用したラムダ式"); };
lam.run(); // 「Runnable を利用したラムダ式」を出力
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// ラムダ式の定義
add_sub it_add = (x, y) -> { return x + y; }; // 既に定義されている変数は不可
add_sub it_sub = (x, y) -> { return x - y; }; // 既に定義されている変数は不可
// ラムダ式をメソッドの引数
sub(it_add); // 13 を出力
sub(it_sub); // -3 を出力
}
static void sub(add_sub it) {
System.out.println(it.func(5, 8));
}
}
// インタフェース add_sub
interface add_sub {
public int func(int x, int y); // 抽象メソッド
}
/****************************/
/* ニュートン法 */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
import java.io.*;
// main
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
double eps1 = 1.0e-7;
double eps2 = 1.0e-10;
double x0 = 0.0;
int max = 30;
int ind[] = new int [1];
// f(x) = exp(x) - 3.0 * x = 0 の解
// 関数値を計算するラムダ式の定義
diff kn1 = (x1) -> { return Math.exp(x1) - 3.0 * x1; };
diff kn2 = (x1) -> { return Math.exp(x1) - 3.0; };
// ニュートン法の実行
double x = Math_ex.newton(x0, eps1, eps2, max, ind, kn1, kn2);
// 出力
System.out.printf("exp(x) - 3.0 * x = 0\n");
System.out.printf(" ind = %d, x = %.3f, f(x) = %.3f, f'(x) = %.3f\n", ind[0], x, kn1.func(x), kn2.func(x));
// f(x) = sin(x) - 0.5 = 0 の解
// 関数値を計算するラムダ式の定義
diff kn3 = (x1) -> { return Math.sin(x1) - 0.5; };
diff kn4 = (x1) -> { return Math.cos(x1); };
// ニュートン法の実行
x = Math_ex.newton(x0, eps1, eps2, max, ind, kn3, kn4);
// 出力
System.out.printf("sin(x) - 0.5 = 0\n");
System.out.printf(" ind = %d, x = %.3f, f(x) = %.3f, f'(x) = %.3f\n", ind[0], 180*x/Math.PI, kn3.func(x), kn4.func(x));
}
}
// インタフェース diff
interface diff {
public double func(double x); // 抽象メソッド
}
--------------------------------
/************************
/* 科学技術計算用の手法 */
/************************/
public final class Math_ex {
/*****************************************************/
/* Newton法による非線形方程式(f(x)=0)の解 */
/* x1 : 初期値 */
/* eps1 : 終了条件1(|x(k+1)-x(k)|<eps1) */
/* eps2 : 終了条件2(|f(x(k))|<eps2) */
/* max : 最大試行回数 */
/* ind : 実際の試行回数 */
/* (負の時は解を得ることができなかった) */
/* kn1 : 関数を計算するラムダ式 */
/* kn2 : 関数の微分を計算するラムダ式 */
/* return : 解 */
/*****************************************************/
static double newton(double x1, double eps1, double eps2, int max,
int ind[], diff kn1, diff kn2)
{
double x = x1;
int sw = 0;
ind[0] = 0;
while (sw == 0 && ind[0] >= 0) {
ind[0]++;
sw = 1;
double g = kn1.func(x1);
if (Math.abs(g) > eps2) {
if (ind[0] <= max) {
double dg = kn2.func(x1);
if (Math.abs(dg) > eps2) {
x = x1 - g / dg;
if (Math.abs(x-x1) > eps1 && Math.abs(x-x1) > eps1*Math.abs(x)) {
x1 = x;
sw = 0;
}
}
else
ind[0] = -1;
}
else
ind[0] = -1;
}
}
return x;
}
}
public static void main(String args[])
java Test 2 3


/***********************************/
/* main メソッドの引数(数字の和) */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/***********************************/
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
/*
引数の内容の出力
*/
System.out.println(" 引数の数 " + args.length);
int sum = 0;
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < args.length; i1++) {
int k = Integer.parseInt(args[i1]); // 文字を整数に変換
System.out.println(" " + (i1+1) + " 番目の引数 " + k);
sum += k;
}
/*
結果の表示
*/
System.out.println("結果=" + sum);
}
}
引数の数 2
1 番目の引数 2
2 番目の引数 3
結果=5
package パッケージ名;
public class {
・・・・
}
/****************************/
/* パッケージ */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
import java.io.*;
public class Sansho
{
public static void main (String[] args)
{
test.Complex x = new test.Complex (1.0, 2.0);
test.Complex y = new test.Complex ();
System.out.print("x = " + "(" + x.real() + "," +
x.imag() + ") abs " + x.v + "\n");
System.out.print("y = " + "(" + y.real() + "," +
y.imag() + ") abs " + y.v + "\n");
}
}
--------------------------------------------
/***********************/
/* クラスComplexの定義 */
/***********************/
package test;
public class Complex // public宣言をしないと,他のパッケージからアクセスできない
// (クラス内の変数,メソッドについても同様)
{
private double r;
private double i;
public double v;
public Complex (double a, double b) // constructor
{
r = a;
i = b;
v = Math.sqrt(a * a + b * b);
}
public Complex () // constructor
{
r = 0;
i = 0;
v = 0.0;
}
public double real() { return r;}
public double imag() { return i;}
}
import java.io.*;
import test.Complex;
public class Sansho
{
public static void main (String[] args)
{
Complex x = new Complex (1.0, 2.0);
Complex y = new Complex ();
System.out.print("x = " + "(" + x.real() + "," +
x.imag() + ") abs " + x.v + "\n");
System.out.print("y = " + "(" + y.real() + "," +
y.imag() + ") abs " + y.v + "\n");
}
}

feed : 原料の供給 add : 2 つの原料を混ぜる product: 反応を行う

/****************************/
/* プラントモデル */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
import java.io.*;
/********************/
/* クラスFeedの定義 */
/********************/
class Feed { /* 原料の供給 */
double x, y, z;
// コンストラクタ
Feed(double x, double y, double z)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.z = z;
}
// 出力
void print()
{
System.out.println("x " + x + " y " + y + " z " + z + " (feed)");
}
}
/*******************/
/* クラスAddの定義 */
/*******************/
class Add { /* 混合 */
double x, y, z;
// コンストラクタ
Add(Feed a, Feed b)
{
x = a.x + b.x;
y = a.y + b.y;
z = a.z + b.z;
}
// 出力
void print()
{
System.out.println("x " + x + " y " + y + " z " + z + " (add)");
}
}
/***********************/
/* クラスProductの定義 */
/***********************/
class Product { /* 製品 */
double x, y, z;
// コンストラクタ
Product(Add a)
{
x = 0.1 * a.x;
y = 0.2 * a.y;
z = 0.9 * a.x + 0.8 * a.y;
}
// 出力
void print()
{
System.out.println("x " + x + " y " + y + " z " + z + " (product)");
}
}
/**************************************/
/* mainメソッドを含むクラスTestの定義 */
/**************************************/
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
Feed feed1 = new Feed (10.0, 20.0, 0.0);
feed1.print();
Feed feed2 = new Feed (5.0, 10.0, 0.0);
feed2.print();
Add add1 = new Add (feed1, feed2);
add1.print();
Product pro1 = new Product (add1);
pro1.print();
}
}
x 10.0 y 20.0 z 0.0 (feed) x 5.0 y 10.0 z 0.0 (feed) x 15.0 y 30.0 z 0.0 (add) x 1.5 y 6.0 z 37.5 (product)

/****************************/
/* ベクトルの内積と大きさ */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
import java.io.*;
/**********************/
/* Vectorクラスの定義 */
/**********************/
class Vector {
int n;
double v[];
/******************/
/* コンストラクタ */
/******************/
Vector (int n)
{
this.n = n;
v = new double [n];
}
/**********/
/* 大きさ */
/**********/
double norm()
{
double x = 0.0;
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < n; i1++)
x += v[i1] * v[i1];
return Math.sqrt(x);
}
/*********************/
/* 内積 */
/* b : ベクトル */
/*********************/
double naiseki(Vector b)
{
double x = 0.0;
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < n; i1++)
x += v[i1] * b.v[i1];
return x;
}
/********/
/* 入力 */
/********/
void input() throws IOException
{
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < n; i1++) {
System.out.print(" " + (i1+1) + "番目の要素は? ");
v[i1] = Double.parseDouble(in.readLine());
}
}
}
/**************************************/
/* mainメソッドを含むクラスTestの定義 */
/*************************************/
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
Vector a = new Vector (2);
Vector b = new Vector (2);
System.out.println("a");
a.input();
System.out.println("b");
b.input();
System.out.println("a と b の内積 " + a.naiseki(b));
System.out.println("a,及び,b の大きさ " + a.norm() + " " + b.norm());
}
}

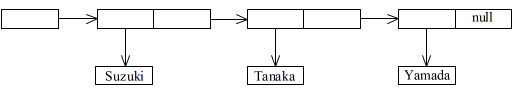
001 /****************************/
002 /* リスト構造 */
003 /* coded by Y.Suganuma */
004 /****************************/
005 import java.io.*;
006
007 /********************/
008 /* クラスListの定義 */
009 /********************/
010 class List
011 {
012 String st; // データ(文字列)
013 List next; // 次のデータ
014 // コンストラクタ
015 List () { }
016
017 List (String s)
018 {
019 st = new String(s);
020 }
021
022 /**************************************/
023 /* データの追加 */
024 /* dt : Listクラスのオブジェクト */
025 /**************************************/
026 void add(List dt)
027 {
028 List lt2 = this;
029 int sw = 1;
030
031 while (sw > 0) {
032 // 最後に追加
033 if (lt2.next == null) {
034 lt2.next = dt;
035 sw = 0;
036 }
037 // 比較し,途中に追加
038 else {
039 List lt1 = lt2;
040 lt2 = lt2.next;
041 int k = dt.st.compareTo(lt2.st); // 比較
042 if (k < 0) { // 追加
043 dt.next = lt2;
044 lt1.next = dt;
045 sw = 0;
046 }
047 }
048 }
049 }
050
051 /*********************/
052 /* データの削除 */
053 /* st1 : 文字列 */
054 /*********************/
055 void del(String st1)
056 {
057 List lt2 = this;
058 int sw = 1;
059
060 while (sw > 0) {
061 // データが存在しない場合
062 if (lt2.next == null) {
063 System.out.println(" 指定されたデータがありません!");
064 sw = 0;
065 }
066 // 比較し,削除
067 else {
068 List lt1 = lt2;
069 lt2 = lt2.next;
070 int k = st1.compareTo(lt2.st); // 比較
071 if (k == 0) { // 削除
072 lt1.next = lt2.next;
073 sw = 0;
074 }
075 }
076 }
077 }
078
079 /**********************/
080 /* リストデータの出力 */
081 /**********************/
082 void output()
083 {
084 List nt = this.next;
085 while (nt != null) {
086 System.out.println(" data = " + nt.st);
087 nt = nt.next;
088 }
089 }
090 }
091
092 /**************************************/
093 /* mainメソッドを含むクラスTestの定義 */
094 /**************************************/
095 public class Test
096 {
097 public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException
098 {
099 BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
100 List name = new List ();
101 int sw = 1;
102
103 while (sw > 0) {
104 String st;
105 System.out.print("1:追加,2:削除,3:出力,0:終了? ");
106 sw = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
107 switch (sw) {
108 case 1: // 追加
109 System.out.print(" データを入力してください ");
110 st = in.readLine();
111 List lt = new List (st);
112 name.add(lt);
113 break;
114 case 2: // 削除
115 System.out.print(" データを入力してください ");
116 st = in.readLine();
117 name.del(st);
118 break;
119 case 3: // 出力
120 name.output();
121 break;
122 default :
123 sw = 0;
124 break;
125 }
126 }
127 }
128 }
/****************************/
/* リスト構造 */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Test
{
public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException
{
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
TreeSet <String> name = new TreeSet <String> ();
String st;
int sw = 1;
while (sw > 0) {
System.out.print("1:追加,2:削除,3:出力,0:終了? ");
sw = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
switch (sw) {
case 1: // 追加
System.out.print(" データを入力してください ");
st = in.readLine();
name.add(st);
break;
case 2: // 削除
System.out.print(" データを入力してください ");
st = in.readLine();
name.remove(st);
break;
case 3: // 出力
Iterator it = name.iterator();
while (it.hasNext())
System.out.println(" data = " + it.next());
break;
default :
sw = 0;
break;
}
}
}
}



| 情報学部 | 菅沼ホーム | 全体目次 | 演習解答例 | 付録 | 索引 |