
| 情報学部 | 菅沼ホーム | 全体目次 | 演習解答例 | 付録 | 索引 |

この章では,配列について説明します.Java にはポインタという言葉(概念)はありませんが,int や double などの基本形以外のデータはすべてポインタで表現されていると考えた方が妥当です.したがって,Java を勉強する場合にも,ポインタという考え方は重要だと思います.そこで,ポインタやアドレスといった言葉についても説明していきます.
int *x = new int; // int* x = new int; でも可 int *y = new int[5]; // int* y = new int[5]; でも可,5個の要素からなる配列とほぼ同等

&value
int *point; // int* point; でも可
point = &value;
char *pc; // char *pc; でも可 double *pd; // double *pd; でも可
data = *point;
*point = 100;
double x, y = 10, *yp = &y; x = *yp;

int x[]; // int [] x; でも可,C++ では,int *x; に相当 double y[]; // double [] y; でも可,C++ では,double *y; に相当
配列の型 配列名[];
x = new int [5]; // C++ では,x = new int [5]; に相当 int x[] = new int [5]; // int [] x = new int [5]; でも可,C++ では,int *x = new int [5]; に相当
int x[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; // int [] x = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; でも可
x[2] = 10; y = x[3];
for (i1 = 0; i1 < 99; i1++) // i1 の値に注意 y[i1] = x[i1+1];
 ( A ~ D の部分を可能な限り一つの変数,定数,演算子等で,埋めてください.その際,文字を削除してから,正しい答えを半角文字で,かつ,余分なスペースを入れないで入力してください.)
( A ~ D の部分を可能な限り一つの変数,定数,演算子等で,埋めてください.その際,文字を削除してから,正しい答えを半角文字で,かつ,余分なスペースを入れないで入力してください.)
/********************************/
/* 平均点の計算と平均点以下の人 */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/********************************/
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[])
{
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
double mean1, mean2, sum1 = 0.0, sum2 = 0.0;
int n, m = 0, i1, no[], x[], y[];
String line;
StringTokenizer str;
try {
// 人数の読み込みと配列の定義
System.out.print("人数は? ");
n = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
no = new int [n];
x = new int [n];
y = new int [n];
// データの読み込みと点数の和の計算
for (i1 = 0; i1 < n; i1++) {
System.out.print("学籍番号,英語の点,数学の点は? ");
line = in.readLine();
str = new StringTokenizer(line, " ");
no[i1] = Integer.parseInt(str.nextToken());
x[i1] = Integer.parseInt(str.nextToken());
y[i1] = Integer.parseInt(str.nextToken());
sum1 += x[i1];
sum2 += y[i1];
}
// 平均点の計算と平均点以下の人
if (n <= 0)
System.out.println("データが存在しません!");
else {
mean1 = sum1 / n;
mean2 = sum2 / n;
System.out.println("英語平均 " + mean1 + " 数学平均 " + mean2);
System.out.println("いずれかの科目が平均点以下の人の学籍番号");
for (i1 = 0; i1 < n; i1++) {
if (x[i1] <= mean1 || y[i1] <= mean2) {
System.out.println(" " + no[i1]);
m++;
}
}
System.out.println("該当学生数 " + m + " 人");
}
}
catch (IOException ignored) {}
}
}

01 /****************************/
02 /* 平方根の計算 */
03 /* coded by Y.Suganuma */
04 /****************************/
05 import java.io.*;
06
07 public class Test {
08 public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
09 {
10 BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
11 double data = 0.0;
12 double x[] = new double [100];
13 double y[] = new double [100];
14 /*
15 平方根の計算
16 */
17 for (int i1 = 0; i1 < 100; i1++) {
18 data += 1.0;
19 x[i1] = data;
20 y[i1] = Math.sqrt(data);
21 }
22 /*
23 ファイル名の入力
24 */
25 System.out.print("出力ファイル名は? ");
26 String f_name = in.readLine();
27 /*
28 出力
29 */
30 PrintStream out = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream(f_name));
31 for (int i1 = 0; i1 < 100; i1++)
32 out.println(x[i1] + " " + y[i1]);
33 out.close();
34 }
35 }

01 /****************************/
02 /* 大文字から小文字への変換 */
03 /* coded by Y.Suganuma */
04 /****************************/
05 import java.io.*;
06
07 public class Test {
08 public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
09 {
10 BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
11 /*
12 データの入力
13 */
14 System.out.print("大文字の文字列を入力してください ");
15 String str = in.readLine();
16 /*
17 小文字へ変換と出力
18 */
19 char c[] = str.toCharArray();
20 for (int i1 = 0; i1 < c.length; i1++)
21 c[i1] += 32;
22 str = new String(c);
23 // str = str.toLowerCase();
24 System.out.println(str);
25 }
26 }

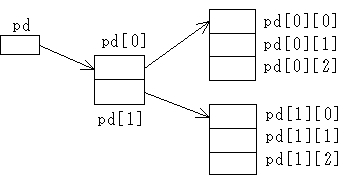
double pd[][] = new double [2][3];
double pd[][] = new double [2][]; // この行以下の 3 行のような形でも可能
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < 2; i1++)
pd[i1] = new double [3]; // 行毎に列数を変えることも可能
double pd[][] = {{1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}}; // 初期設定を行う場合
double x1[] = {1, 2, 3}; // これ以下の方法で初期設定も可能
double x2[] = {4, 5, 6};
double pd[][] = {x1, x2}; double x[] = pd[1];
 ( A ~ D の部分を可能な限り一つの変数,定数,演算子等で,埋めてください.その際,文字を削除してから,正しい答えを半角文字で,かつ,余分なスペースを入れないで入力してください.)
( A ~ D の部分を可能な限り一つの変数,定数,演算子等で,埋めてください.その際,文字を削除してから,正しい答えを半角文字で,かつ,余分なスペースを入れないで入力してください.)
/********************************/
/* 平均点の計算と平均点以下の人 */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/********************************/
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[])
{
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
double mean1, mean2, sum1 = 0.0, sum2 = 0.0;
int n, m = 0, x[][];
String line;
StringTokenizer str;
try {
// 人数の読み込みと配列の定義
System.out.print("人数は? ");
n = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
x = new int [n][3];
// データの読み込みと点数の和の計算
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < n; i1++) {
System.out.print("学籍番号,英語の点,数学の点は? ");
line = in.readLine();
str = new StringTokenizer(line, " ");
x[i1][0] = Integer.parseInt(str.nextToken());
x[i1][1] = Integer.parseInt(str.nextToken());
x[i1][2] = Integer.parseInt(str.nextToken());
sum1 += x[i1][1];
sum2 += x[i1][2];
}
// 平均点の計算と平均点以下の人
if (n <= 0)
System.out.println("データが存在しません!");
else {
mean1 = sum1 / n;
mean2 = sum2 / n;
System.out.println("英語平均 " + mean1 + " 数学平均 " + mean2);
System.out.println("いずれかの科目が平均点以下の人の学籍番号");
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < n; i1++) {
if (x[i1][1] <= mean1 || x[i1][2] <= mean2) {
System.out.println(" " + x[i1][0]);
m++;
}
}
System.out.println("該当学生数 " + m + " 人");
}
}
catch (IOException ignored) {}
}
}

/****************************/
/* 配列とポインタ */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
/****************/
/* main program */
/****************/
public static void main(String args[])
{
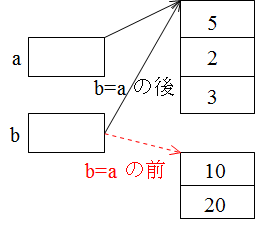
int a[] = new int [3];
int b[] = new int [2];
// 値を設定
a[0] = 1;
a[1] = 2;
a[2] = 3;
b[0] = 10;
b[1] = 20;
// a,bの出力
System.out.println("a " + a[0] + " " + a[1] + " " + a[2]);
// System.out.println("b " + b[0] + " " + b[1] + " " + b[2]); エラー
System.out.println("b " + b[0] + " " + b[1]);
// aをbに代入(配列aのアドレスをbに代入)
b = a;
// bの出力
System.out.println("b(aをbに代入後) " + b[0] + " " + b[1] + " " + b[2]);
// a[0]の値の変更
a[0] = 5;
// a,bの出力
System.out.println("a(a[0]の値を変更後) " + a[0] + " " + a[1] + " " + a[2]);
System.out.println("b(a[0]の値を変更後) " + b[0] + " " + b[1] + " " + b[2]);
}
}
a 1 2 3 b 10 20 b(aをbに代入後) 1 2 3 a(a[0]の値を変更後) 5 2 3 b(a[0]の値を変更後) 5 2 3
cl.val ( cl がポインタでない場合) cl->val ( cl がポインタである場合)
| 配列型 | 初期値 |
|---|---|
| byte | 0 |
| short | 0 |
| int | 0 |
| long | 0L |
| float | 0.0f |
| double | 0.0d |
| char | '\u0000' |
| boolean | false |
| 参照型(オブジェクト型) | NULL |

01 /****************************************/
02 /* 1 次元配列,初期設定,及び,ポインタ */
03 /* coded by Y.Suganuma */
04 /****************************************/
05 import java.io.*;
06
07 public class Test {
08 public static void main(String args[])
09 {
10 /*
11 初期設定された値と確保された領域のサイズ
12 */
13 int x2[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}; // 6つのデータ領域
14 for (int i1 = 0; i1 < x2.length; i1++)
15 System.out.print(x2[i1] + " ");
16 System.out.print("(" + 4*x2.length + "バイト)\n");
17
18 String c1 = "test data"; // 文字列
19 String c2[] = {"test1 data", "test2 data"}; // 2つの文字列
20 System.out.println(c1 + "(" + 2*c1.length() + "バイト)");
21 for (int i1 = 0; i1 < c2.length; i1++)
22 System.out.println(c2[i1] + "(" + 2*c2[i1].length() + "バイト)");
23 /*
24 要素の参照と変更
25 */
26 int x1[] = x2; // int x1[] は,配列であることの宣言
27 x1[1] = -1;
28 x2[3] = -3;
29 for (int i1 = 0; i1 < x2.length; i1++)
30 System.out.print(x2[i1] + " ");
31 System.out.print("\n");
32
33 c1 = "test0 data";
34 System.out.println(c1 + "(" + 2*c1.length() + "バイト)");
35 c2[0] = "test100 data";
36 for (int i1 = 0; i1 < c2.length; i1++)
37 System.out.println(c2[i1] + "(" + 2*c2[i1].length() + "バイト)");
38 }
39 }
1 2 3 4 5 6 (24バイト) test data(18バイト) test1 data(20バイト) test2 data(20バイト) 1 -1 3 -3 5 6 test0 data(20バイト) test100 data(24バイト) test2 data(20バイト)

int px1[]; // int [] px1; でも可 int px2[][]; // int [][] px2; でも可
int *px1; int **px2;
01 /****************************************/
02 /* 多次元配列,初期設定,及び,ポインタ */
03 /* coded by Y.Suganuma */
04 /****************************************/
05 import java.io.*;
06
07 public class Test {
08 public static void main(String args[])
09 {
10 /*
11 初期設定された値と確保された領域のサイズ
12 */
13 int x1[][] = {{1, 2}, {3, 4}, {5, 6}}; // 3行2列(初期化)
14 System.out.println(x1[1][1] + "(" + 4*x1.length + "バイト)");
15
16 String c1[] = {"zero", "one", "two", "three"}; // Stringの一次元配列
17 for (int i1 = 0; i1 < c1.length; i1++)
18 System.out.println(c1[i1] + "(" + 2*c1[i1].length() + "バイト)");
19 /*
20 要素の参照と変更
21 */
22 int px1[] = x1[2]; // 配列 x1 の 3 行目の先頭アドレス
23 int px2[][] = x1; // 配列 x1 のアドレス
24 System.out.println(x1[2][1] + " " + px1[1] + " " + px2[2][1]);
25 }
26 }
4(12バイト) zero(8バイト) one(6バイト) two(6バイト) three(10バイト) 6 6 6

01 /****************************/
02 /* new 演算子と代入・初期化 */
03 /* coded by Y.Suganuma */
04 /****************************/
05 import java.io.*;
06 import java.util.*;
07
08 public class Test {
09 public static void main(String args[])
10 {
11 // 単純変数
12 System.out.println("***単純変数***");
13 int a1 = 0;
14 int a2 = a1;
15 a1 = 1234;
16 System.out.printf(" a1 %d\n", a1);
17 System.out.printf(" a2 %d\n", a2);
18 // 配列
19 System.out.println("***配列***");
20 int p2[] = {1, 2, 3, 4};
21 int p5[] = p2;
22 int pc[] = p2.clone();
23 Complex x1 = new Complex();
24 Complex x2 = new Complex();
25 Complex u5[] = {x1, x2}, u6[];
26 u6 = u5.clone();
27 p2[2] = 200;
28 u6[0] = new Complex();
29 u6[0].x = 6;
30 u6[1].x = 7;
31 System.out.printf(" p2");
32 for (int i1 = 0; i1 < 4; i1++)
33 System.out.printf(" %d", p2[i1]);
34 System.out.printf("\n p5");
35 for (int i1 = 0; i1 < 4; i1++)
36 System.out.printf(" %d", p5[i1]);
37 System.out.printf("\n pc");
38 for (int i1 = 0; i1 < 4; i1++)
39 System.out.printf(" %d", pc[i1]);
40 System.out.printf("\n u5");
41 for (int i1 = 0; i1 < 2; i1++)
42 System.out.printf(" (%d %d)", u5[i1].x, u5[i1].y);
43 System.out.printf("\n u6");
44 for (int i1 = 0; i1 < 2; i1++)
45 System.out.printf(" (%d %d)", u6[i1].x, u6[i1].y);
46 // クラスのオブジェクト
47 System.out.println("\n***クラスのオブジェクト***");
48 Complex p3 = new Complex();
49 Complex p6 = p3;
50 p3.x = 20;
51 System.out.printf(" p3 %d %d\n", p3.x, p3.y);
52 System.out.printf(" p6 %d %d\n", p6.x, p6.y);
53 // String クラス
54 System.out.println("***String クラス***");
55 String s1 = new String("abc");
56 String s2 = s1;
57 s1 = s1.replace('a', 'X');
58 System.out.printf(" s1 %s\n", s1);
59 System.out.printf(" s2 %s\n", s2);
60 // ArrayList クラス
61 System.out.println("***ArrayList クラス***");
62 ArrayList <String> a = new ArrayList <String> ();
63 a.add("abc");
64 ArrayList <String> b = a;
65 ArrayList <String> c = new ArrayList <String> (a);
66 ArrayList <String> d = listCast(a.clone());
67 // ArrayList <String> d = (ArrayList <String>)a.clone();
68 System.out.printf(" a (size) %d (contens) %s\n", a.size(), a.get(0));
69 System.out.printf(" b (size) %d (contens) %s\n", b.size(), b.get(0));
70 System.out.printf(" c (size) %d (contens) %s\n", c.size(), c.get(0));
71 System.out.printf(" d (size) %d (contens) %s\n", d.size(), d.get(0));
72 a.add("xyz");
73 System.out.printf(" a (size) %d (contens) %s %s\n", a.size(), a.get(0), a.get(1));
74 System.out.printf(" b (size) %d (contens) %s %s\n", b.size(), b.get(0), b.get(1));
75 System.out.printf(" c (size) %d (contens) %s\n", c.size(), c.get(0));
76 System.out.printf(" d (size) %d (contens) %s\n", d.size(), d.get(0));
77 }
78
79 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
80 public static <Type> Type listCast(Object src) {
81 Type target = (Type)src;
82 return target;
83 }
84 }
85
86 /*****************/
87 /* クラスComplex */
88 /*****************/
89 class Complex
90 {
91 int x, y;
92 Complex()
93 {
94 x = 0;
95 y = 0;
96 }
97 }
***単純変数*** a1 1234 a2 0
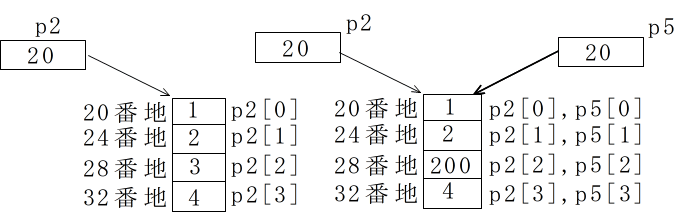
***配列*** p2 1 2 200 4 p5 1 2 200 4 pc 1 2 3 4 u5 (0 0) (7 0) u6 (6 0) (7 0)
***クラスのオブジェクト*** p3 20 0 p6 20 0
***String クラス*** s1 Xbc s2 abc
***ArrayList クラス*** a (size) 1 (contens) abc b (size) 1 (contens) abc c (size) 1 (contens) abc d (size) 1 (contens) abc a (size) 2 (contens) abc xyz b (size) 2 (contens) abc xyz c (size) 1 (contens) abc d (size) 1 (contens) abc
RANGE NUM 0- 10 2 ** 11- 20 5 ***** ・・・・ 91-100 3 ***
*
* *
* * ・・・・・ * *
* * * * *
-------------- ・・・・・ ---------
1 2 3 ・・・・・ 11 12
| 情報学部 | 菅沼ホーム | 全体目次 | 演習解答例 | 付録 | 索引 |