
| 情報学部 | 菅沼ホーム | 全体目次 | 演習解答例 | 付録 | 索引 |

class Example {
int x; // プライベートメンバー変数
・・・
protected:
int y; // 派生クラスだけが使用可能なメンバー変数
・・・
public:
int z; // パブリックメンバー変数
・・・
private:
double fun1(int); // プライベートメンバー関数
・・・
protected:
double fun2(int); // 派生クラスだけが使用可能なメンバー関数
・・・
public:
double fun3(int); // パブリックメンバー関数
・・・
friend double fun4(int); // フレンド関数
・・・
friend class Example2; // フレンドクラス
・・・
};
Example ex; // Example 型オブジェクトの生成 EXample *p_ex = new Example; // p_ex は Example 型オブジェクトへのポインタ ex.x = 20; // メンバー変数 x の参照 y = p_ex->func(10); // ポインターによるメンバー関数 func の参照 Example ex1 = ex; // ex の内容がコピーされて ex1 に代入 EXample *p_ex1 = p_ex; // p_ex1 は p_ex と同じオブジェクトを指す
01 #include <stdio.h>
02
03 class Example {
04 static int s1;
05 public:
06 static int s2;
07 static void out() { printf("from out s1 %d s2 %d\n", s1, s2); }
08 };
09
10 int Example::s1 = 10; // static 指定のため必要
11 int Example::s2 = 20; // static 指定のため必要
12
13 int main()
14 {
15 printf("from main s2 %d\n", Example::s2); // s1 は参照不可
16 Example::out();
17 Example t;
18 printf("from main s2 %d\n", t.s2); // s1 は参照不可
19 t.out();
20 return 0;
21 }
クラス名::静的メンバー変数名 クラス名::静的メンバー関数名
/****************************/
/* クラスの宣言 */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/***********************/
/* クラスExampleの宣言 */
/***********************/
class Example {
int x; // private メンバー変数
public:
int y; // public メンバー変数
void v_set1() // public メンバー関数
{
x = 10;
y = 20;
}
void v_set2() // public メンバー関数
{
x = 30;
y = 40;
}
void output() // public メンバー関数
{
cout << " x = " << x << ", y = " << y << endl;
}
}; // 「;」が必要なことに注意
/*************/
/* main 関数 */
/*************/
int main()
{
Example t1; // Example 型オブジェクト
Example *t2 = new Example; // Example 型オブジェクトへのポインタ
t1.v_set1(); // メンバー関数の呼び出し
t2->v_set2(); // メンバー関数の呼び出し
cout << "オブジェクト t1\n";
cout << " y = " << t1.y << endl; // 変数xへのアクセスはできない
t1.output();
cout << "オブジェクト t2\n";
cout << " y = " << t2->y << endl; // 変数xへのアクセスはできない
t2->output();
return 0;
}
オブジェクト t1 y = 20 x = 10, y = 20 オブジェクト t2 y = 40 x = 30, y = 40
class C2;
class C1 {C2 *p; ・・・};
class C2 {C1 *q; ・・・};
関数の型 クラス名::関数名 (引数のリスト)
{
・・・・・
}
friend int func(Example &,・・・);
friend int Example1::func(Example &,・・・);
friend class List;
01 #include <iostream>
02
03 using namespace std;
04
05 class Test {
06 int x = 10;
07 int y = 20;
08 int ct = 0;
09 public:
10 Test() {} // コンストラクタ1
11 void print()
12 // void print() const // メンバー変数を変更できない
13 {
14 ct++;
15 cout << "x " << x << " y " << y << " ct " << ct << endl;
16 }
17 };
18
19 int main()
20 {
21 Test t;
22 t.print();
23 t.print();
24
25 return 0;
26 }
/******************************/
/* メンバー関数とフレンド関数 */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/******************************/
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/***********************/
/* クラスExampleの定義 */
/***********************/
class Example {
int x;
public:
int y;
void set(int, int);
friend void fun1(Example &);
};
void fun2(Example &);
/************/
/* main関数 */
/************/
int main()
{
Example data; // dataがExample型のオブジェクトであることを宣言
data.set(10, 20); // メンバー関数の呼び出し.ピリオドに注意
fun1(data); // フレンド関数の呼び出し
fun2(data); // 普通の関数の呼び出し
return 0;
}
/*********************************************/
/* メンバー関数 */
/* プログラム例10.1のようにクラス定義の */
/* 内部に記述することもできる */
/*********************************************/
void Example::set(int a, int b)
{
x = a;
this->y = b; // y = b と同じ
cout << "x " << x << " y " << y << endl;
}
/****************/
/* フレンド関数 */
/****************/
void fun1(Example &data)
{
cout << "x " << data.x << " y " << data.y << endl;
}
/**************/
/* 普通の関数 */
/**************/
void fun2(Example &data)
{
cout << "x ??" << " y " << data.y << endl; // xにはアクセスできない
}
メンバー関数 x 10 y 20 フレンド関数 x 10 y 20 通常の関数 x ?? y 20 フレンドクラス x 10 y 20
t1.v_set1(); t2->v_set2();
Example(int x1, int y1)
{
x = x1;
y = y1;
}
// 以下のように,メンバー初期設定リストを使用しても良い
Example(int x1, int y1) : x(x1), y(y1) {} Example t1(10, 20); // Example 型オブジェクト Example *t2 = new Example (30, 40); // Example 型オブジェクトへのポインタ
001 #include <iostream>
002 #include <vector>
003 #include <initializer_list>
004
005 using namespace std;
006
007 class Test {
008 public:
009 int x = 1000; // 非静的メンバ変数の初期化(C++11)
010 int y[3];
011 vector<int> v1;
012 vector<int> v2;
013 // コンストラクタ1(メンバー初期設定リストを利用)
014 Test(int x1, int y1[], initializer_list<int> in1, initializer_list<int> in2) :
015 // explicit Test(int x1, int y1[], initializer_list<int> in1, initializer_list<int> in2) :
016 x(x1), y(), v1(in1.begin(), in1.end()), v2(in2.begin(), in2.end()) {
017 for (int i1 = 0; i1 < 3; i1++)
018 y[i1] = y1[i1];
019 cout << "(コンストラクタ 1)\n";
020 }
021 // コンストラクタ2(メンバー初期設定リストを利用しない)
022 Test(int x1, int y1[], vector<int> vv1, vector<int> vv2) {
023 // explicit Test(int x1, int y1[], vector<int> vv1, vector<int> vv2) {
024 x = x1; // この文がなければ,x の値は 1000 のまま
025 for (int i1 = 0; i1 < 3; i1++)
026 y[i1] = y1[i1];
027 for (const auto& e : vv1)
028 v1.push_back(e);
029 for (const auto& e : vv2)
030 v2.push_back(e);
031 cout << "(コンストラクタ 2)\n";
032 }
033 };
034
035 void func(int x[]) {
036 cout << " function";
037 for (int i1 = 0; i1 < 3; i1++)
038 cout << " " << x[i1];
039 cout << endl;
040 }
041
042 void func(vector<int> x) {
043 cout << " function";
044 for (auto e : x)
045 cout << " " << e;
046 cout << endl;
047 }
048
049 int main()
050 {
051 // 配列
052 int x[] {1, 2, 3};
053 // int x[] = {1, 2, 3}; // ok
054 cout << "** 配列 x **\n";
055 for (auto e : x)
056 cout << " " << e;
057 cout << endl;
058 func(x);
059 // func({1, 2, 3}); // error
060
061 int *y = new int [3] {1, 2, 3};
062 cout << "** 配列 y (new) **\n";
063 for (int i1 = 0; i1 < 3; i1++)
064 cout << " " << y[i1];
065 cout << endl;
066 // vector
067 vector<int> v1 {1, 2, 3};
068 // vector<int> v1 = {1, 2, 3}; // ok
069 cout << "** vector v1 **\n";
070 for (auto e : v1)
071 cout << " " << e;
072 cout << endl;
073 func(v1);
074 // func({1, 2, 3}); // ok
075
076 vector<int> *v2 = new vector<int> {1, 2, 3};
077 cout << "** vector v2 **\n";
078 for (int i1 = 0; i1 < 3; i1++)
079 cout << " " << (*v2)[i1];
080 cout << endl;
081 // クラス Test のオブジェクト
082 int ty[] = {4, 5, 6};
083
084 cout << "** class Test ** ";
085 Test t1 {100, ty, {10, 20, 30}, {1, 2, 3}}; // コンストラクタ1,及び,2 で ok
086 // Test t1 = {100, ty, {10, 20, 30}, {1, 2, 3}}; // explicit を付けた場合は不可,以下の記述であれば良い
// Test t1(100, ty, {10, 20, 30}, {1, 2, 3});
087 cout << " x: " << t1.x << " y:";
088 for (auto e : t1.y)
089 cout << " " << e;
090 cout << " v1:";
091 for (auto e : t1.v1)
092 cout << " " << e;
093 cout << " v2:";
094 for (auto e : t1.v2)
095 cout << " " << e;
096 cout << endl;
097
098 cout << "** class Test ** ";
099 vector<int> tv1 = {10, 20, 30};
100 vector<int> tv2 = {1, 2, 3};
101 Test t2 {100, ty, tv1, tv2}; // コンストラクタ1 では不可,コンストラクタ2 で ok
102 // Test t2 = {100, ty, tv1, tv2}; // explicit を付けた場合は不可,以下の記述であれば良い
// Test t1(100, ty, tv1, tv2);
103 cout << " x: " << t2.x << " y:";
104 for (auto e : t2.y)
105 cout << " " << e;
106 cout << " v1:";
107 for (auto e : t2.v1)
108 cout << " " << e;
109 cout << " v2:";
110 for (auto e : t2.v2)
111 cout << " " << e;
112 cout << endl;
113
114 return 0;
115 }
** 配列 x **
1 2 3
function 1 2 3
** 配列 y (new) **
1 2 3
** vector v1 **
1 2 3
function 1 2 3
** vector v2 **
1 2 3
** class Test ** (コンストラクタ 1)
x: 100 y: 4 5 6 v1: 10 20 30 v2: 1 2 3
** class Test ** (コンストラクタ 2)
x: 1000 y: 4 5 6 v1: 10 20 30 v2: 1 2 3
/****************************/
/* 時間データの処理 */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
#include <stdio.h>
/********************/
/* クラスTimeの宣言 */
/********************/
class Time {
int hour, min, sec;
public:
// コンストラクタ,2つの引数はデフォルト
Time(int h, int m = 0, int s = 0)
{
hour = h;
min = m;
sec = s;
}
// 以下のように,メンバー初期設定リストを使用しても良い
// Time(int h, int m = 0, int s = 0) : hour(h), min(m), sec(s) {}
// コンストラクタ.引数無しも許可.このように引数の異なる
// 宣言を許す場合は,デフォルト引数又は関数名のオーバーロードが必要
Time() {}
// 出力
void print()
{
printf("%2d:%2d:%2d\n", hour, min, sec);
}
};
/************/
/* main関数 */
/************/
int main()
{
Time time1(10, 20, 23); // 10:20:23
Time time2 = Time(12, 30); // 12:30:00
Time time3; // 初期設定されない(内容は不定)
time1.print();
time2.print();
time3.print();
return 0;
}
10:20:23 12:30: 0 6749984:1970558921:6750032
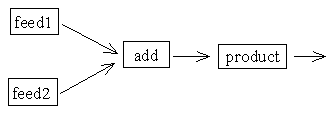
feed : 原料の供給 add : 2 つの原料を混ぜる product: 反応を行う
/****************************/
/* プラントモデル */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
#include <stdio.h>
/********************/
/* クラスFeedの定義 */
/********************/
class Feed { /* 原料の供給 */
public:
double x, y, z;
// コンストラクタ
Feed(double a, double b, double c)
{
x = a;
y = b;
z = c;
}
// 出力
void print()
{
printf("x %f y %f z %f (feed)\n", x, y, z);
}
};
/*******************/
/* クラスAddの定義 */
/*******************/
class Add { /* 混合 */
public:
double x, y, z;
// コンストラクタ
Add(Feed &a, Feed &b)
{
x = a.x + b.x;
y = a.y + b.y;
z = a.z + b.z;
}
// 出力
void print()
{
printf("x %f y %f z %f (add)\n", x, y, z);
}
};
/***********************/
/* クラスProductの定義 */
/***********************/
class Product { /* 製品 */
public:
double x, y, z;
// コンストラクタ
Product(Add &a)
{
x = 0.1 * a.x;
y = 0.2 * a.y;
z = 0.9 * a.x + 0.8 * a.y;
}
// 出力
void print()
{
printf("x %f y %f z %f (product)\n", x, y, z);
}
};
/************/
/* main関数 */
/************/
int main()
{
Feed feed1(10.0, 20.0, 0.0);
feed1.print();
Feed feed2(5.0, 10.0, 0.0);
feed2.print();
Add add1(feed1, feed2);
add1.print();
Product pro1(add1);
pro1.print();
return 0;
}
x 10.000000 y 20.000000 z 0.000000 (feed) x 5.000000 y 10.000000 z 0.000000 (feed) x 15.000000 y 30.000000 z 0.000000 (add) x 1.500000 y 6.000000 z 37.500000 (product)
/****************************/
/* ベクトルの内積と絶対値 */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
/**********************/
/* Vectorクラスの定義 */
/**********************/
class Vector {
public:
int n;
double *v;
Vector (int n1) // コンストラクタ
{
n = n1;
v = new double [n];
}
~Vector() // デストラクタ
{
if (n > 0)
delete [] v;
}
double zettai(); // 絶対値
double naiseki(Vector &); // 内積
void input(); // 要素の入力
};
/**********/
/* 絶対値 */
/**********/
double Vector::zettai()
{
double x = 0.0;
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < n; i1++)
x += v[i1] * v[i1];
return sqrt(x);
}
/*********************/
/* 内積 */
/* b : ベクトル */
/*********************/
double Vector::naiseki(Vector &b)
{
double x = 0.0;
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < n; i1++)
x += v[i1] * b.v[i1];
return x;
}
/********/
/* 入力 */
/********/
void Vector::input()
{
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < n; i1++) {
cout << " " << i1+1 << "番目の要素は? ";
cin >> v[i1];
}
}
/******************/
/* mainプログラム */
/******************/
int main()
{
Vector a(2), b(2);
cout << "a\n";
a.input();
cout << "b\n";
b.input();
cout << "内積 " << a.naiseki(b) << endl;
cout << "絶対値 " << a.zettai() << " " << b.zettai() << endl;
return 0;
}
a 1番目の要素は? 1 2番目の要素は? 2 b 1番目の要素は? 2 2番目の要素は? 5 内積 12 絶対値 2.23607 5.38516
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <numeric>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// 初期設定
vector<double> v1 {1, 2, 3};
cout << "v1 :";
for (auto x : v1)
cout << " " << x;
cout << endl;
vector<double> v2 {2, 3, 4};
cout << "v2 :";
for (auto x : v2)
cout << " " << x;
cout << endl;
double s1 = inner_product(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), 0);
double s2 = sqrt(inner_product(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v1.begin(), 0));
cout << " v1 と v2 の内積 = " << s1 << ", 絶対値(v1) = " << s2 << endl;
return 0;
}
/****************************/
/* リスト構造 */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
/********************/
/* クラスListの定義 */
/********************/
class List
{
char *st;
List *next;
public :
// コンストラクタ
List () { next = NULL; }
List (char *s)
{
next = NULL;
st = new char [strlen(s)+1];
strcpy(st, s);
}
void add(List *); // データの追加
void del(char *); // データの削除
void output(); // 出力
};
/**************************************/
/* データの追加 */
/* dt : Listクラスのオブジェクト */
/**************************************/
void List::add(List *dt)
{
List *lt2 = this;
int sw = 1;
while (sw > 0) {
// 最後に追加
if (lt2->next == NULL) {
lt2->next = dt;
sw = 0;
}
// 比較し,途中に追加
else {
List *lt1 = lt2;
lt2 = lt2->next;
int k = strcmp(dt->st, lt2->st); // 比較
if (k < 0) { // 追加
dt->next = lt2;
lt1->next = dt;
sw = 0;
}
}
}
}
/*********************/
/* データの削除 */
/* st1 : 文字列 */
/*********************/
void List::del(char *st1)
{
List *lt2 = this;
int sw = 1;
while (sw > 0) {
// データが存在しない場合
if (lt2->next == NULL) {
printf(" 指定されたデータがありません!\n");
sw = 0;
}
// 比較し,削除
else {
List *lt1 = lt2;
lt2 = lt2->next;
int k = strcmp(st1, lt2->st); // 比較
if (k == 0) { // 削除
lt1->next = lt2->next;
sw = 0;
}
}
}
}
/**********************/
/* リストデータの出力 */
/**********************/
void List::output()
{
List *nt = this->next;
while (nt != NULL) {
printf(" data = %s\n", nt->st);
nt = nt->next;
}
}
/****************/
/* main program */
/****************/
int main ()
{
int sw = 1;
char st[100];
List base, *lt;
while (sw > 0) {
printf("1:追加,2:削除,3:出力,0:終了? ");
scanf("%d", &sw);
switch (sw) {
case 1: // 追加
printf(" データを入力してください ");
scanf("%s", st);
lt = new List(st);
base.add(lt);
break;
case 2: // 削除
printf(" データを入力してください ");
scanf("%s", st);
base.del(st);
break;
case 3: // 出力
base.output();
break;
default :
sw = 0;
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
1:追加,2:削除,3:出力,0:終了? 1 データを入力してください xyz 1:追加,2:削除,3:出力,0:終了? 1 データを入力してください sdd 1:追加,2:削除,3:出力,0:終了? 1 データを入力してください abc 1:追加,2:削除,3:出力,0:終了? 2 データを入力してください sdd 1:追加,2:削除,3:出力,0:終了? 3 data = abc data = xyz 1:追加,2:削除,3:出力,0:終了? 0
/****************************/
/* リスト処理 */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
/**********************/
/* リストデータの出力 */
/* lt : リスト */
/**********************/
void output(set<string> &s) {
set<string>::iterator it;
cout << "要素数: " << s.size() << "\n";
for (it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); it++)
cout << " " << *it;
cout << "\n";
}
/****************/
/* main program */
/****************/
int main ()
{
int sw = 1;
string str;
set <string> s;
while (sw > 0) {
cout << "1:追加,2:削除,3:出力,0:終了? ";
cin >> sw;
switch (sw) {
case 1: // 追加
cout << " データを入力してください ";
cin >> str;
s.insert(str);
break;
case 2: // 削除
cout << " データを入力してください ";
cin >> str;
s.erase(str);
break;
case 3: // 出力
output(s);
break;
default :
sw = 0;
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
001 /****************************/
002 /* 様々なデータ型の引き渡し */
003 /* coded by Y.Suganuma */
004 /****************************/
005 #include <iostream>
006 using namespace std;
007
008 /***********************/
009 /* クラスComplexの定義 */
010 /***********************/
011 class Complex {
012 public:
013 double re, im;
014 int *a;
015 // コンストラクタ
016 Complex(double re, double im, int x)
017 {
018 this->re = re;
019 this->im = im;
020 this->a = new int [1];
021 this->a[0] = x;
022 }
023 };
024
025 /*****************************************************/
026 /* 関数の例 */
027 /* a, b, c : int 型 */
028 /* ar_11, ar_12 : int 型 1 次元配列 */
029 /* ar_21, ar_22, ar_23 : int 型 2 次元配列 */
030 /* cx1, cx2, cx3 : Complex クラスのオブジェクト */
031 /*****************************************************/
032 void method(int a, int *b, int &c, int ar_11[], int *ar_12, int ar_21[][3], int **ar_22,
int *ar_23, Complex cx1, Complex *cx2, Complex &cx3)
033 {
034 a = 9;
035 *b = 9;
036 c = 9;
037 ar_11[0] = 99;
038 ar_12[0] = 99; // *ar_12 = 99;
039 ar_21[1][0] = 999;
040 ar_22[1][0] = 999;
041 ar_23[3] = 999;
042 cx1.im = 9999;
043 cx1.a[0] = 555;
044 cx2->im = 9999;
045 cx2->a[0] = 555;
046 cx3.im = 9999;
047 cx3.a[0] = 555;
048 }
049
050 /*************/
051 /* main 関数 */
052 /*************/
053 int main()
054 {
055 int a = 1, b = 1, c = 1;
056 int ar_11 [] = {10, 20};
057 int *ar_12 = new int [2];
058 ar_12[0] = 10;
059 ar_12[1] = 20;
060 int ar_21 [][3] = {{100, 200, 300}, {400, 500, 600}};
061 int **ar_22 = new int * [2];
062 for (int i1 = 0; i1 < 2; i1++) {
063 ar_22[i1] = new int [3];
064 for (int i2 = 0; i2 < 3; i2++) {
065 if (i1 == 0)
066 ar_22[i1][i2] = 100 * (i2 + 1);
067 else
068 ar_22[i1][i2] = 100 * (i2 + 4);
069 }
070 }
071 int ar_23 [][3] = {{100, 200, 300}, {400, 500, 600}};
072 Complex cx1(1000, 2000, 3000);
073 Complex cx2(1000, 2000, 3000);
074 Complex cx3(1000, 2000, 3000);
075 // 関数をcall前
076 cout << " ***関数をcall前***\n";
077 cout << "a = " << a << " b = " << b << " c = " << c << endl;
078 cout << "ar_11[0] = " << ar_11[0] << ", ar_11[1] = " << ar_11[1] << endl;
079 cout << "ar_12[0] = " << ar_12[0] << ", ar_12[1] = " << ar_12[1] << endl;
080 for (int i1 = 0; i1 < 2; i1++) {
081 for (int i2 = 0; i2 < 3; i2++) {
082 if (i2 < 2)
083 cout << "ar_21[" << i1 << "][" << i2 << "] = " << ar_21[i1][i2] << ", ";
084 else
085 cout << "ar_21[" << i1 << "][" << i2 << "] = " << ar_21[i1][i2] << endl;
086 }
087 }
088 for (int i1 = 0; i1 < 2; i1++) {
089 for (int i2 = 0; i2 < 3; i2++) {
090 if (i2 < 2)
091 cout << "ar_22[" << i1 << "][" << i2 << "] = " << ar_22[i1][i2] << ", ";
092 else
093 cout << "ar_22[" << i1 << "][" << i2 << "] = " << ar_22[i1][i2] << endl;
094 }
095 }
096 for (int i1 = 0; i1 < 2; i1++) {
097 for (int i2 = 0; i2 < 3; i2++) {
098 if (i2 < 2)
099 cout << "ar_23[" << i1 << "][" << i2 << "] = " << ar_23[i1][i2] << ", ";
100 else
101 cout << "ar_23[" << i1 << "][" << i2 << "] = " << ar_23[i1][i2] << endl;
102 }
103 }
104 cout << "cx1.re = " << cx1.re << ", cx1.im = " << cx1.im << ", cx1.a[0] = " << cx1.a[0] << endl;
105 cout << "cx2.re = " << cx2.re << ", cx2.im = " << cx2.im << ", cx2.a[0] = " << cx2.a[0] << endl;
106 cout << "cx3.re = " << cx3.re << ", cx3.im = " << cx3.im << ", cx3.a[0] = " << cx3.a[0] << endl;
107 // 関数をcall
108 method(a, &b, c, ar_11, ar_12, ar_21, ar_22, &ar_23[0][0], cx1, &cx2, cx3);
109 // 関数をcall後
110 cout << " ***関数をcall後***\n";
111 cout << "a = " << a << " b = " << b << " c = " << c << endl;
112 cout << "ar_11[0] = " << ar_11[0] << ", ar_11[1] = " << ar_11[1] << endl;
113 cout << "ar_12[0] = " << ar_12[0] << ", ar_12[1] = " << ar_12[1] << endl;
114 for (int i1 = 0; i1 < 2; i1++) {
115 for (int i2 = 0; i2 < 3; i2++) {
116 if (i2 < 2)
117 cout << "ar_21[" << i1 << "][" << i2 << "] = " << ar_21[i1][i2] << ", ";
118 else
119 cout << "ar_21[" << i1 << "][" << i2 << "] = " << ar_21[i1][i2] << endl;
120 }
121 }
122 for (int i1 = 0; i1 < 2; i1++) {
123 for (int i2 = 0; i2 < 3; i2++) {
124 if (i2 < 2)
125 cout << "ar_22[" << i1 << "][" << i2 << "] = " << ar_22[i1][i2] << ", ";
126 else
127 cout << "ar_22[" << i1 << "][" << i2 << "] = " << ar_22[i1][i2] << endl;
128 }
129 }
130 for (int i1 = 0; i1 < 2; i1++) {
131 for (int i2 = 0; i2 < 3; i2++) {
132 if (i2 < 2)
133 cout << "ar_23[" << i1 << "][" << i2 << "] = " << ar_23[i1][i2] << ", ";
134 else
135 cout << "ar_23[" << i1 << "][" << i2 << "] = " << ar_23[i1][i2] << endl;
136 }
137 }
138 cout << "cx1.re = " << cx1.re << ", cx1.im = " << cx1.im << ", cx1.a[0] = " << cx1.a[0] << endl;
139 cout << "cx2.re = " << cx2.re << ", cx2.im = " << cx2.im << ", cx2.a[0] = " << cx2.a[0] << endl;
140 cout << "cx3.re = " << cx3.re << ", cx3.im = " << cx3.im << ", cx3.a[0] = " << cx3.a[0] << endl;
141 return 0;
142 }
01 ***関数をcall前*** 02 a = 1 b = 1 c = 1 03 ar_11[0] = 10, ar_11[1] = 20 04 ar_12[0] = 10, ar_12[1] = 20 05 ar_21[0][0] = 100, ar_21[0][1] = 200, ar_21[0][2] = 300 06 ar_21[1][0] = 400, ar_21[1][1] = 500, ar_21[1][2] = 600 07 ar_22[0][0] = 100, ar_22[0][1] = 200, ar_22[0][2] = 300 08 ar_22[1][0] = 400, ar_22[1][1] = 500, ar_22[1][2] = 600 09 ar_23[0][0] = 100, ar_23[0][1] = 200, ar_23[0][2] = 300 10 ar_23[1][0] = 400, ar_23[1][1] = 500, ar_23[1][2] = 600 11 cx1.re = 1000, cx1.im = 2000, cx1.a[0] = 3000 12 cx2.re = 1000, cx2.im = 2000, cx2.a[0] = 3000 13 cx3.re = 1000, cx3.im = 2000, cx3.a[0] = 3000 14 ***関数をcall後*** 15 a = 1 b = 9 c = 9 16 ar_11[0] = 99, ar_11[1] = 20 17 ar_12[0] = 99, ar_12[1] = 20 18 ar_21[0][0] = 100, ar_21[0][1] = 200, ar_21[0][2] = 300 19 ar_21[1][0] = 999, ar_21[1][1] = 500, ar_21[1][2] = 600 20 ar_22[0][0] = 100, ar_22[0][1] = 200, ar_22[0][2] = 300 21 ar_22[1][0] = 999, ar_22[1][1] = 500, ar_22[1][2] = 600 22 ar_23[0][0] = 100, ar_23[0][1] = 200, ar_23[0][2] = 300 23 ar_23[1][0] = 999, ar_23[1][1] = 500, ar_23[1][2] = 600 24 cx1.re = 1000, cx1.im = 2000, cx1.a[0] = 555 25 cx2.re = 1000, cx2.im = 9999, cx2.a[0] = 555 26 cx3.re = 1000, cx3.im = 9999, cx3.a[0] = 555

| 情報学部 | 菅沼ホーム | 全体目次 | 演習解答例 | 付録 | 索引 |