/****************************/
/* 大人と子どもの識別 */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int nenrei;
/*
年齢の入力
*/
System.out.print("年齢を入力してください ");
nenrei = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
/*
判断
*/
if (nenrei >= 20)
System.out.println(" 大人");
else
System.out.println(" 子供");
}
}
/****************************/
/* 正,負,ゼロの識別 */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int kazu;
/*
年齢の入力
*/
System.out.print("数字を入力してください ");
kazu = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
/*
判断
*/
if (kazu == 0)
System.out.println(" 0");
else {
if (kazu > 0)
System.out.println(" 正");
else
System.out.println(" 負");
}
}
}
/****************************/
/* 成績の判定 */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int ten;
/*
点数の入力
*/
System.out.print("点数は? ");
ten = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
/*
判定
*/
if (ten < 60)
System.out.println(" 不可");
else {
if (ten < 70)
System.out.println(" 可");
else {
if (ten < 80)
System.out.println(" 良");
else
System.out.println(" 優");
}
}
}
}
/****************************/
/* 時間の変換 */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int time, min, sw;
/*
変換方法の入力
*/
System.out.print("変換方法は(0:時間→分, 1:分→時間)? ");
sw = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
/*
データと変換
*/
if (sw == 0) {
System.out.print("時間は? ");
time = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
System.out.print("分は? ");
min = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
min = 60 * time + min;
System.out.println(" " + min + " 分です");
}
else {
System.out.print("分は? ");
min = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
time = min / 60;
min = min % 60;
System.out.println(" " + time + " 時間 " + min + " 分です");
}
}
}
/****************************/
/* 閏年の判定 */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int year;
/*
年の入力
*/
System.out.print("年を入力して下さい? ");
year = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
/*
判定
*/
if (((year%4 == 0) && (year%100 != 0)) || (year%400 == 0))
System.out.println(" 閏年です");
else
System.out.println(" 閏年ではありません");
}
}
/***************************/
/* 正弦の計算 */
/* coded by Y.Suganum */
/***************************/
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[])
{
double pi, unit, x, y;
int i1;
/*
初期設定
*/
pi = 4.0 * Math.atan(1.0);
unit = pi / 180.0;
x = 0.0;
/*
計算と出力
*/
for (i1 = 1; i1 <= 90; i1++) {
x += 1.0;
y = Math.sin(x * unit);
System.out.println("角度 " + x + " 正弦 " + y);
}
}
}
/***************************/
/* 2乗和等の計算 */
/* coded by Y.Suganum */
/***************************/
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[])
{
double sum1, sum2, x;
int i1;
/*
初期設定
*/
sum1 = 0.0;
sum2 = 0.0;
/*
計算
*/
x = 0.0;
for (i1 = 0; i1 < 500; i1++) {
x += 1.0;
sum1 += x * x;
}
x = 0.0;
for (i1 = 0; i1 < 20; i1++) {
x += 1.0;
sum2 += 1.0 / x;
}
/*
出力
*/
System.out.println("和=" + sum1 + " " + sum2);
}
}
/**************************************/
/* 100以上,及び,100未満のデータの和 */
/* coded by Y.Suganum */
/**************************************/
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int i1, n, sum1, sum2, x;
/*
初期設定
*/
sum1 = 0;
sum2 = 0;
/*
データの数の入力
*/
System.out.print("データの数は? ");
n = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
/*
計算
*/
for (i1 = 0; i1 < n; i1++) {
System.out.print("データは? ");
x = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
if (x < 100)
sum1 += x;
else
sum2 += x;
}
/*
出力
*/
System.out.println("100未満の和 " + sum1 + " 100以上の和 " + sum2);
}
}
/***************************/
/* 正と負の数の個数 */
/* coded by Y.Suganum */
/***************************/
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int i1, n, sei, hu, x;
/*
初期設定
*/
sei = 0;
hu = 0;
/*
データの数の入力
*/
System.out.print("データの数は? ");
n = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
/*
データを入力し数える
*/
for (i1 = 0; i1 < n; i1++) {
System.out.print("データは? ");
x = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
if (x != 0) {
if (x > 0)
sei++;
else
hu++;
}
}
/*
出力
*/
System.out.println("正の数 " + sei + " 負の数 " + hu);
}
}
/***************************/
/* 抵抗の直列と並列 */
/* coded by Y.Suganum */
/***************************/
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
double cho, hei, x;
int i1, n;
/*
初期設定
*/
cho = 0.0;
hei = 0.0;
/*
データの数の入力
*/
System.out.print("抵抗の数は? ");
n = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
/*
抵抗の計算
*/
for (i1 = 0; i1 < n; i1++) {
System.out.print(" 抵抗の値は? ");
x = Double.parseDouble(in.readLine());
cho += x;
hei += 1.0 / x;
}
hei = 1.0 / hei;
/*
出力
*/
System.out.println("直列結合 " + cho + " 並列結合 " + hei);
}
}
/****************************/
/* n!の計算 */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
double kai;
int i1, n;
/*
初期設定
*/
kai = 1.0;
/*
nの入力
*/
System.out.print("nの値は? ");
n = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
if (n < 0)
System.out.println("データが不適当です!");
/*
計算
*/
else {
for (i1 = 2; i1 <= n; i1++)
kai *= i1;
/*
出力
*/
System.out.println(" n!=" + kai);
}
}
}
/****************************/
/* nCrの計算 */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
double c, nk, rk, n_rk;
int i1, n, r;
/*
データの入力
*/
System.out.print("nは? ");
n = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
System.out.print("rは? ");
r = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
if (n < 0 || r < 0 || r > n)
System.out.println("データが不適当です!");
/*
実行
*/
else {
nk = 1.0;
for (i1 = 2; i1 <= n; i1++)
nk *= i1;
rk = 1.0;
for (i1 = 2; i1 <= r; i1++)
rk *= i1;
n_rk = 1.0;
for (i1 = 2; i1 <= (n-r); i1++)
n_rk *= i1;
c = nk / (rk * n_rk);
System.out.println(" nCr= " + c);
}
}
}
/****************************/
/* 3n+1 */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int n;
/*
nの入力
*/
System.out.print("nの値は? ");
n = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
System.out.println(" n=" + n);
/*
計算
*/
while (n > 1) {
if (n%2 == 0)
n = n / 2;
else
n = 3 * n + 1;
System.out.println(" n=" + n);
}
}
}
/****************************/
/* 優、良、可、不可の割合 */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
double a0, a1, a2, a3;
int i1, m, n;
/*
初期設定
*/
a0 = 0.;
a1 = 0.;
a2 = 0.;
a3 = 0.;
/*
入力
*/
System.out.print("人数は? ");
n = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
for (i1 = 0; i1 < n; i1++) {
System.out.print(" 点数は ");
m = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
if (m < 50)
a0 += 1.;
else {
if (m < 60)
a1 += 1.;
else {
if (m < 80)
a2 += 1.;
else
a3 += 1.;
}
}
}
/*
計算と出力
*/
a0 = a0 / n * 100.;
a1 = a1 / n * 100.;
a2 = a2 / n * 100.;
a3 = a3 / n * 100.;
System.out.println("不可=" + a0);
System.out.println(" 可=" + a1);
System.out.println(" 良=" + a2);
System.out.println(" 優=" + a3);
}
}
/****************************/
/* 給与の計算 */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("kyuyo"));
int i1, kyuyo, k1, n, m10000, m5000, m1000, m500, m100;
/*
初期設定
*/
m10000 = 0;
m5000 = 0;
m1000 = 0;
m500 = 0;
m100 = 0;
/*
データの読み込みと計算
*/
n = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
for (i1 = 0; i1 < n; i1++) {
kyuyo = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
k1 = kyuyo / 10000;
kyuyo -= k1 * 10000;
m10000 += k1;
k1 = kyuyo / 5000;
kyuyo -= k1 * 5000;
m5000 += k1;
k1 = kyuyo / 1000;
kyuyo -= k1 * 1000;
m1000 += k1;
k1 = kyuyo / 500;
kyuyo -= k1 * 500;
m500 += k1;
k1 = kyuyo / 100;
m100 += k1;
}
/*
出力
*/
System.out.println("10000円札 " + m10000 + " 枚");
System.out.println("5000円札 " + m5000 + " 枚");
System.out.println("1000円札 " + m1000 + " 枚");
System.out.println("500円硬貨 " + m500 + " 枚");
System.out.println("100円硬貨 " + m100 + " 枚");
in.close();
}
}
/****************************/
/* 九九の表の出力 */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int i1, i2, k;
for (i1 = 1; i1 <= 9; i1++) {
for (i2 = 1; i2 <= 9; i2++) {
k = i1 * i2;
if (k < 10)
System.out.print(" " + k);
else
System.out.print(" " + k);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
/****************************/
/* 数字の分離 */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
int n, m, k = 100000000, k1, sw = 0;
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.print("正の整数を入力してください ");
n = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
// 正順
m = n;
while (k > 0) {
k1 = m / k;
m %= k;
k /= 10;
if (k1 > 0) {
sw = 1;
System.out.print(k1 + " ");
}
else {
if (sw > 0)
System.out.print(k1 + " ");
}
}
System.out.println();
// 逆順
m = n;
while (m > 0) {
k1 = m % 10;
m /= 10;
System.out.print(k1 + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
/****************************/
/* 1のビット数を数える */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int i1, n, kazu = 0;
int mask = 0x80000000;
/*
整数の入力
*/
System.out.print("整数を入力して下さい ");
n = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
/*
個数を数える
*/
for (i1 = 0; i1 < 32; i1++) {
if ((mask & n) != 0)
kazu++;
mask >>>= 1;
}
System.out.println("1のビット数は " + kazu);
}
}
/************************************/
/* 最大値と最小値の計算(未知個数) */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/************************************/
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("input"));
double max = 0, min = 0, x;
int sw = 0;
String str;
/*
データの入力と比較
*/
while (null != (str = in.readLine())) {
x = Double.parseDouble(str);
if (sw == 0) {
sw = 1;
max = x;
min = x;
}
else {
if (x > max)
max = x;
else {
if (x < min)
min = x;
}
}
}
/*
結果の出力
*/
System.out.println("最大値= " + max + " 最小値= " + min);
}
}
/****************************/
/* 最高点とそのクラス */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int i1, i2, max, max_c = 0, n, m, ten;
/*
初期設定
*/
max = 0;
/*
データの入力と計算
*/
System.out.print("クラスの数は? ");
n = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
for (i1 = 0; i1 < n; i1++) {
System.out.print((i1+1) + " 番目のクラスの人数は ");
m = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
for (i2 = 0; i2 < m; i2++) {
System.out.print(" " + (i2+1) + " 番目の人の点は? ");
ten = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
if (ten > max) {
max_c = i1 + 1;
max = ten;
}
}
}
/*
出力
*/
System.out.println("最高点はクラス " + max_c + " の " + max + " 点");
}
}

/****************************/
/* ニュートン法 */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
double g, dg, eps1, eps2, x, x0, x1, s, ds;
int max, ind, sw;
/*
データの入力
*/
System.out.print("eps1? ");
eps1 = Double.parseDouble(in.readLine());
System.out.print("eps2? ");
eps2 = Double.parseDouble(in.readLine());
System.out.print("最大試行回数? ");
max = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
System.out.print("初期値? ");
x0 = Double.parseDouble(in.readLine());
/*
初期設定
*/
x1 = x0;
x = x1;
ind = 0;
sw = 0;
/*
実行
*/
while (sw == 0 && ind >= 0) {
sw = 1;
ind = ind + 1;
g = Math.exp(x1) - 3.0 * x1;
if (Math.abs(g) > eps2) {
if (ind <= max) {
dg = Math.exp(x1) - 3.0;
if (Math.abs(dg) > eps2) {
x = x1 - g / dg;
if (Math.abs(x-x1) > eps1) {
x1 = x;
sw = 0;
}
}
else
ind = -1;
}
else
ind = -1;
}
}
/*
出力
*/
if (ind < 0)
System.out.println("解を求めることができません!");
else {
s = Math.exp(x) - 3.0 * x;
ds = Math.exp(x) - 3.0;
System.out.println("ind=" + ind + " x=" + x + " f=" + s + " df=" + ds);
}
}
}

/****************************/
/* 二分法 */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
double eps1, eps2, f = 0.0, f1, f2, x = 0.0, x1 = 0.0, x2 = 0.0;
int max, ind, sw;
/*
データの入力
*/
System.out.print("eps1? ");
eps1 = Double.parseDouble(in.readLine());
System.out.print("eps2? ");
eps2 = Double.parseDouble(in.readLine());
System.out.print("最大試行回数? ");
max = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
sw = 0;
while (sw == 0) {
System.out.print("初期値(1つ目)? ");
x1 = Double.parseDouble(in.readLine());
System.out.print("初期値(2つ目)? ");
x2 = Double.parseDouble(in.readLine());
f1 = Math.exp(x1) - 3.0 * x1;
f2 = Math.exp(x2) - 3.0 * x2;
if (f1*f2 < 0.0)
sw = 1;
}
/*
初期設定
*/
f1 = Math.exp(x1) - 3.0 * x1;
f2 = Math.exp(x2) - 3.0 * x2;
ind = 0;
sw = 0;
/*
実行
*/
while (sw == 0 && ind >= 0) {
ind++;
sw = 1;
x = 0.5 * (x1 + x2);
f = Math.exp(x) - 3.0 * x;
if (Math.abs(f) > eps2) {
if (ind <= max) {
if (Math.abs(x1-x2) > eps1) {
sw = 0;
if (f*f1 < 0.0) {
x2 = x;
f2 = f;
}
else {
x1 = x;
f1 = f;
}
}
}
else
ind = -1;
}
}
/*
出力
*/
if (ind < 0)
System.out.println("解を求めることができません!");
else
System.out.println("ind=" + ind + " x=" + x + " f= " + f);
}
}
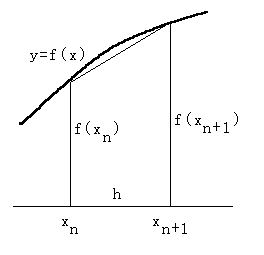
/****************************/
/* 台形則による積分 */
/* coded by Y.Suganuma */
/****************************/
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
double f1, f2, h, s, x, x1, x2;
int i1, n;
/*
データの入力
*/
System.out.print("積分区間の最初は? ");
x1 = Double.parseDouble(in.readLine());
System.out.print("積分区間の最後は? ");
x2 = Double.parseDouble(in.readLine());
System.out.print("分割数は? ");
n = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
/*
初期設定
*/
f1 = Math.exp(-0.5 * x1 * x1) / 2.506628275;
f2 = Math.exp(-0.5 * x2 * x2) / 2.506628275;
s = 0.5 * (f1 + f2);
h = (x2 - x1) / n;
x = x1 + h;
/*
実行
*/
for (i1 = 0; i1 < n-1; i1++) {
s = s + Math.exp(-0.5 * x * x) / 2.506628275;
x = x + h;
}
s = s * h;
/*
出力
*/
System.out.println("面積=" + s);
}
}